Available iPad Apps
-
 Auditory Phonetic Subtraction
Auditory Phonetic Subtraction
-
 Auditory Visual Integration
Auditory Visual Integration
-
 Colourimetry
Colourimetry
-
 Digit Matching
Digit Matching
-
 Dyscalculia
Dyscalculia
-
 Dyseidesia / Dysphonesia
Dyseidesia / Dysphonesia
-
 Dysnemkinesia
Dysnemkinesia
-
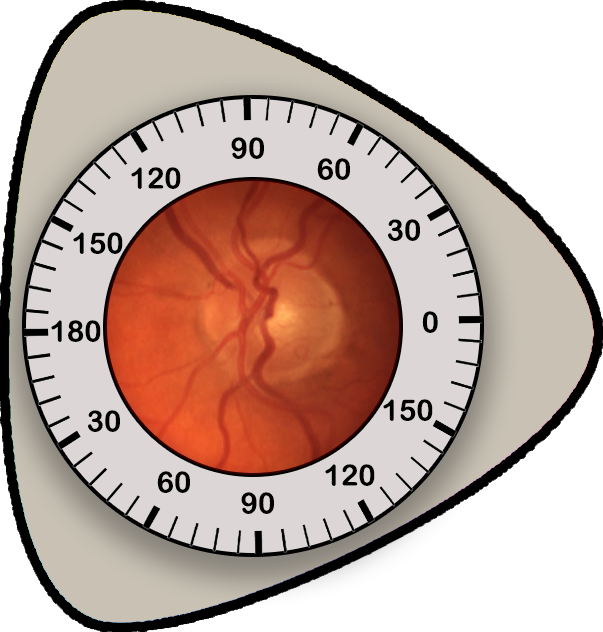 Eye Exam Data
Eye Exam Data
-
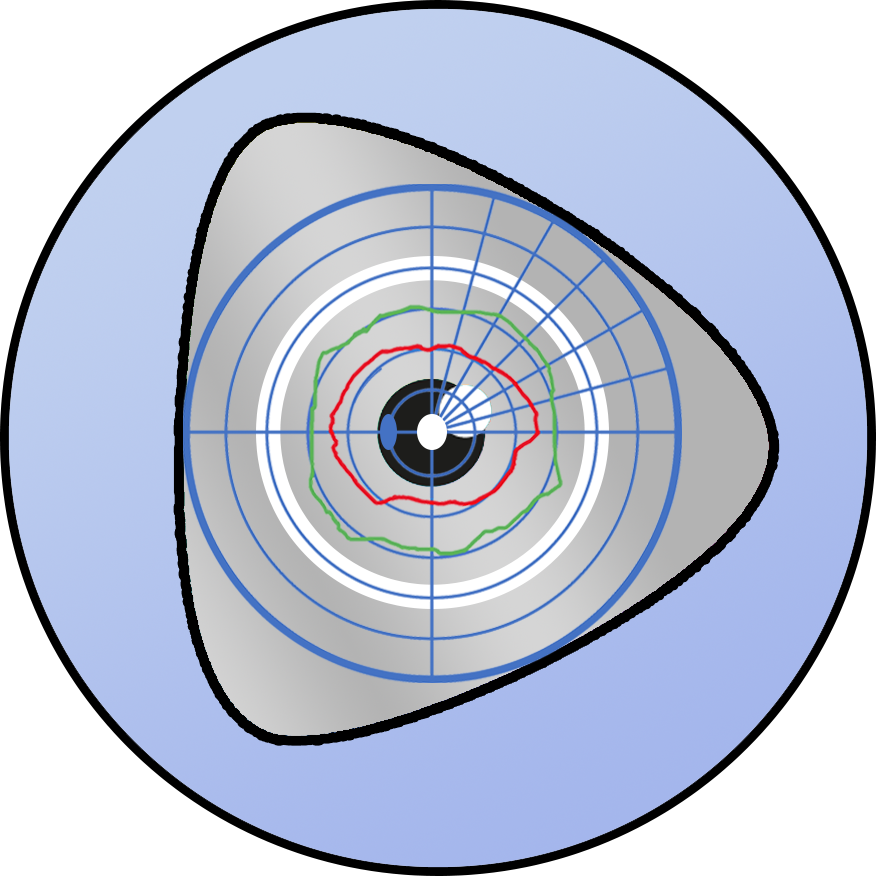 Kinetic Colour Perimetry
Kinetic Colour Perimetry
-
 Laterality
Laterality
-
 Reading Eye Movement
Reading Eye Movement
-
 Retained Reflexes
Retained Reflexes
-
 Sentence Copy
Sentence Copy
-
 Sequencing
Sequencing
-
 Tachistoscope
Tachistoscope
-
 Visual Sensory Perception
Visual Sensory Perception
-
 Visual Spatial Awareness
Visual Spatial Awareness
Dyscalculia
Loosely based on the Australian NAPLAN testing our dyscalculia test is a time sensitive age-based screening assessment for children aged 8-14 years and is designed to assess and identify difficulties related to mathematical abilities and number processing in an individual revealing:
- Core Numerical Skills:
- Number Sense: The ability to understand numerical magnitude and manipulate numbers, including recognizing quantities without counting.
- Basic Arithmetic Skills: Proficiency in performing basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Number Recognition: The ability to recognize and correctly identify numbers.
- Counting Skills: Understanding number sequences and using counting strategies.
- Mathematical Reasoning:
- Problem Solving: The ability to apply mathematical concepts to solve word problems and practical scenarios.
- Understanding Mathematical Concepts: Grasping concepts such as place value, fractions, decimals, and mathematical relationships.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying and extending numerical patterns.
- Cognitive Processes:
- Memory: Working memory and long-term memory for numbers and mathematical procedures.
- Processing Speed: The speed at which the individual can perform mathematical calculations and understand numerical information.
- Spatial and Visual Skills: The ability to understand and manipulate visual representations of mathematical problems, such as graphs, charts, and geometric figures.
- Specific Learning Difficulties:
- Error Patterns: Identifying specific types of errors made consistently, such as miscalculations, reversals, or misinterpretations of problems.
- Strengths and Weaknesses: Highlighting areas of relative strength and pinpointing specific weaknesses that may require targeted intervention.
- Educational Implications:
- Need for Support: Determines if the individual requires extra assessment for implementation of special educational support, tutoring, or accommodations in the classroom.
- Identifies Weaknesses to Help Tailor Intervention Strategies.